Benjamin Park, Archive Assistant discusses his first impressions as a new member of the Theatre Collection and what he has learned from his colleagues around him.
I joined the Theatre Collection during the middle of September as a maternity cover for one of the Archive Assistants. It is the first time I have worked in an archive and the past couple of months has been an insightful period, full of discoveries and curiosities.
I was not a stranger to archives before this, and neither a stranger to the Theatre Collection. My background was varied, and many threads seemed to lead me here. Prior to this role I was a Library Assistant, working just up the hill from the Theatre Collection at other sites within the University of Bristol. That was my first experience professionally working with collections. During and before this point, I was a student of literature and most recently a PhD researcher writing on Samuel Beckett. This necessitated many visits to archives and gave me an understanding of their value and function from the perspective of a user. The final thread leading me to this archive was my previous work as an amateur playwright and director in Edinburgh for a span of two years. That experience concreted my respect and admiration for the ephemeral art of theatre. I first discovered the Theatre Collection itself during an oral history research project I undertook with the university. During this project, my fellow researchers and I spent a day in the archive and were introduced to some of their brilliant objects. Later, I interviewed the former Director of the Theatre Collection, Jo Elsworth, in which she showed me a digitised piece of toast from 1994 held by the archive. This innovative piece of marketing was created by Julie Flowers and Rosalind Howell for their performance Grill. I never stopped thinking about that toast and hoped one day to work closer with the Collection.

A Piece of Toast at the National Review of Live Art 1994 by Julie Flowers and Rosalind Howell. [Theatre Collection Reference: RLAP/G/94] A 3D Model of the Toast can be found on Sketchfab.
Fortune was in my favour, and here I am. These months have taught me a lot about archives and collections, and many things that I could only glean hints of before as a user. In my first few weeks, I was introduced to the current team of archivists, and each guided me in their own way to the tips, tricks, and skills required to be a great archivist, as they all are. Jill Sullivan was of particular help in my training and led me to discover the first incredible idiosyncrasy that separates work in an archive collection from my previous work in a library collection, that being the importance of the working mind of an archivist.
As Jill and I would be working on a retrieval together, going through a list of items that a researcher had requested, I would see a sudden flash in her mind as she remembered a particular item of special relevance to the research. An item, tucked away in a folder, in a box amongst hundreds of other boxes.
I would come to learn that the primary and most important role of an archive is to protect and preserve materials to be safely stored in perpetuity. The safety of the item comes first, the next (huge) task is the project of cataloguing so that these items are known, publicly facing, and of easy discovery to researchers and enthusiasts alike. However, the second part of this process takes time, time to secure funding and resources for the detailed cataloguing of these unique collections. Therefore, in archives across the world there are items that are safely stored, waiting for the appropriate funding and allotment of time to be catalogued onto a public-facing database. Bundles of letters, marginalia in private books, early sketches and drawings of obscure artists, and countless other items lay safe on the shelves of many archives, almost a secret. To mitigate this situation, the Theatre Collection currently has a project to box list any uncatalogued collections and it creates web pages and collection-level catalogue descriptions for the public of these collections. But what is most striking to me, is that the collections are intimately known by staff; many of these items are ‘catalogued’ in the working mind of the archivist. At the Theatre Collection, when a person makes an enquiry to explore our holdings and search for material related to their research, in addition to the catalogue, the importance of this mind comes to the fore, unlocking items that may, just possibly, hold the long-searched-for secret to their question. Only three months in, it will probably take me quite a few many more months, if not years, to get close to the working knowledge of some of the archivists here.
Although in that time, what I have discovered has been brilliant and fascinating. And I have learned that that working knowledge can only be obtained by getting lost in the archive yourself. Each week, the researchers, students, historians, working dramaturgs, and other enthusiasts have their items retrieved for their visits. This is one of the highlights of my week. I must always fight against my own curiosity, to retrieve the items in a timely manner, and to not become lost in the interest of their topic. And it is a fight I often almost lose. From Laurence Olivier’s gloves worn in The Entertainer, to Sir Henry Irving’s preparation book for the 1885 production of Faust, to Julia Trevelyan Oman’s designs for chocolate box lids, to hundreds of playbills from the late 18th and 19th centuries, there is an endless stream of wonderful distractions and discoveries during the process of retrievals. The most recent discovery placed before me was the conceptual designs by Ralph Adron for La Creation Du Monde – a ballet by Darius Milhaud which outlines the creation of the world according to African mythologies.
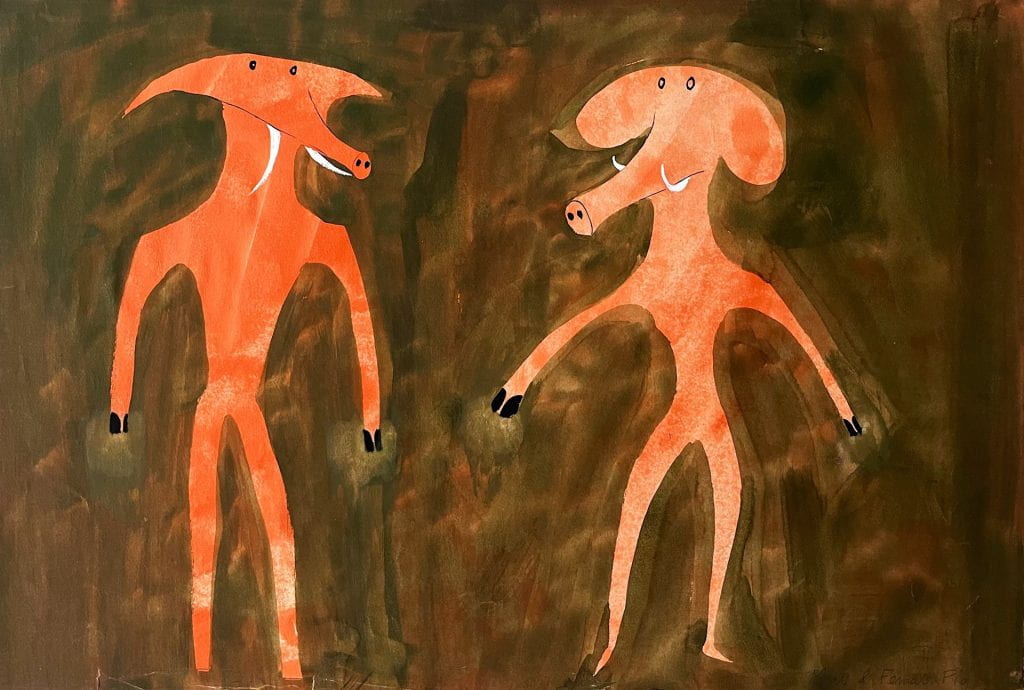 [Conceptual Design by Ralph Adron. Theatre Collection Reference: BTC71/1/6/1/4]
[Conceptual Design by Ralph Adron. Theatre Collection Reference: BTC71/1/6/1/4]
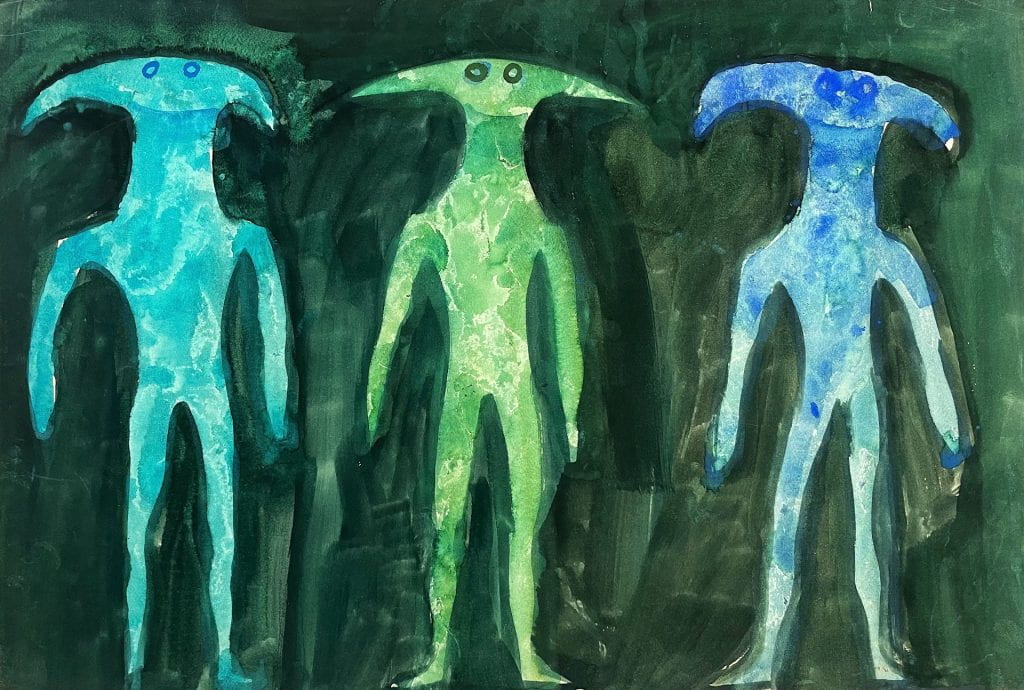

[Conceptual Design by Ralph Adron. Theatre Collection Reference: BTC71/1/6/1/8]
These were brought to my attention during this most recent month, in which the distractions and discoveries of the archive found further use as I took more responsibility in my role managing the Theatre Collection’s social media communications. With immense help and support from the working minds of these archivists, and particularly Laura Dow, the Theatre Collection has shared a range from our wonderful items to our social medias and recently launched Instagram. Two of these items were the above Ralph Adron paintings. This past Monday, as I returned the items that had been taken out for use in the previous week, I picked up these paintings, and felt an instant subconscious thrill at the prospect of what others lay in the drawer they were to be returned to. And as I carefully found the correct position to return each painting to, I discovered a whole host of other fantastic creatures and designs inspired by African creation mythology, and I felt very fortunate have the job that I have.
There is still much more for me to learn in my time here with the Theatre Collection. But as a first lesson I was glad it was this. Namely, the discovery of the living quality of an archive. At times there seems to be an unfortunate public image that archives are rows of dusty shelves filled with untouched tomes. This could not be further from the truth of the true nature of an archive. An archive is a dynamic a living body of materials that must be set in motion as they are explored by researchers and the priceless stories and information contained within them spiral outwards into our collective cultural narrative. And this character of an archive is embodied in the working mind of an archivist, and their particular, irreplaceable relationship to the materials for which they care.




